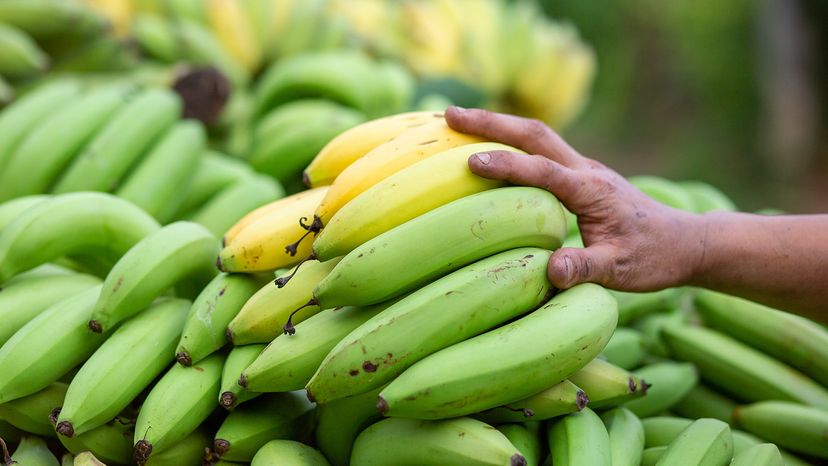
Bananas and plantains come from plants of the same genus (Musa), but the plantain vs. banana comparison boils down to more than just size and skin.
But both bananas and plantains thrive in tropical regions like Southeast Asia, Central and South America, and Caribbean countries.
Advertisement
These edible fruits produced by herbaceous plants may look similar, but they have distinct uses, flavors, and nutritional profiles. While bananas typically show up in your fruit salad, plantains are more likely to appear in a savory dish or be fried to golden perfection.